alternator
Alternator and its Types
(A) Alternator- An a.c. generating machine, is called an alternator or a.c. generator. It is used to generate alternating e.m.f. in accordance with the Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction- 'whenever a conductor is rotated in a magnetic flux, then it cuts the magnetic lines of force, and an e.m.f. is induced in it.' the working principle of an alternator is the same as that of a d.c. generator. an alternator requires a magnetic flux, conductor and the mechanical power for generating the e.m.f. the e.m.f.generated by the alternator is obtained through slip-ring or directly from the stator windings. depending on the type of alternator used. generally the field of an alternator is excited with a d.c. generator, which is mounted on the alternator's shaft. hence an alternator is also known as a separately excited generator.
(B) Types of Alternators-
1. On Basic of prime mover
a. Water Turbine Alternator
b. Steam Turbine Alternator
c. Oil Engine Alternator
2. On Basic of Phases
a. Single Phase Alternator
b. Three Phase Alternator
3. On Basic Of Rotor
1. Rotating Armature Alternator
2. Rotating Field
1. On the Basic of Prime Mover
a. Water Turbine Alternator- In this alternator, the rotor is rotated with the force of water. the water is stored in the form of a small lake,, by making a barrage on a river or canal. then a water-fall is produced with the stored water, which rotates the turbine and which in turn rotates the rotor. the speed of this alternator is low due to low water speed, and thus to obtain the reuired frequency, the number of poles is to be kept more,
b. Steam Turbine Alternator- The force produced by steam is greater than produced by water. the steam operates a steam-engine and the engine operates the alternator. the speed of this alternator in high. A2-pole alternator can generate a frequency of 50 c/s at 3000 R.P.M.
c. Oil Engine Alternator- In this alternator, the rotor is rotated by a diesel or petrol operated engine. since the system is expensive, therefore, it is used for such purposes where water or steam type alternators do not suit or for emergency purposes.
2. On Basic of Phases
a. Single Phase Alternator- A small alternator used to generate the e.m.f. upto 250 volts. for light and fan purposes, is usually single phase type.
b. Three Phase Alternator-This alternator can generate 650 to 6600 or even more. It is used for light and fan as well as for power purposes.
3. on the basis of rotor
(1) Rotating Armature Alternator- It is similar to a generator. it employs slip-rings in place of commutator. the poles are kept stationary, and the armature rotates between the poles. the e.m.f. is obtained through the slip-rings. this alternator, usually has a low output capacity.
(a) Rotating field is comparatively light in weight and hence it can run at a high speed. two slip rings of low current capacity are sufficient for its field excitation circuit.
(b) higher voltage can be generated because of high speed of the rotor.
(c) It is easier to insulate armature coils designed to work at high voltage, because these are placed in the stator portion. if the armature is kept rotating, then the high insulation of armature coils will make it bulky. Hence it will not be able to rotate at a high speed.
(d) the armature winding placed in star or delta system, can directly be connected to the distribution cables.
Advantages of Polyphase Alternator
(a) Polyphase alternator are small in size and economic in comparison to the single phase alternators, having the same output, voltage and frequency.
(b) Polyphase alternator has a constant armature reaction, while a single phase alternator has a pulsating armature reaction under balanced load conditions:
(c) Polyphase transmission lines require less copper, in comparison to single phase transmission lines.
(d) the output power of a polyphase alternator is stable and non-pulsating for balanced loads.
(e) A polyphase alternator has a grater efficiency in comparison to a single phase alternator.
Working Principle Of Alternator
A conducting loop ABCD placed in the magnetic field of N and S poles. the loos is connected to two slip-ring S1 and S2. the a.c. output is taken from the two brushs, which make a sliding contact with the two slip-rings S1 and S2. here AB conductor is in from of N pole and BC conductor is in front of S-pole. since the loop is parallel to the flux thus it does not cut any flux when the loop is rotated in a clockwise direction by 30o , 60o and 90o and so on, then AB conductor cuts the flux in the upward direction while CD conductor cuts in down-ward direction.
the e.m.f. induced in AB part is collected by S1 and that in CD part by S2. the induced e.m.f. reached at its positive peak value in 90o rotation and then it reduced from peak to zero as
after 1800 rotation of the loop, AB conductor reaches in from of S-pole while CD in front of N-pole. now further rotation to (-) 90o produced negative e.m.f. which reaches to negative peak and then back to zero. in this way, the loop completes one cycle. it is evident that the e.m.f. generated is A.C. whose direction and magnitude is changing at a definite rate.
Construction Of Alternator
The parts of an alternator are as follows:
1. Stator 2. Rotor
3. Slipring 4. Exciter
1. Stator- In a rotating field alternator, the stator contains the armature it is house in a cast-iron Yoke. it consists of laminated sheet-sheel cores.
the slots are cut on the whole circumference of the cores as the cores are insulated with varnish or paper and tied together with nutbolts then these are fixed on the yoke or frame. armature winding are placed in the slots the may be cut in various shapes as
2. Rotor- The rotating part of a machine is termed as rotor hare it house the field winding and the poles. rotors are of following two types:
(a) Salient pole type (b) Cylindrical Pole Type
(a) Salient Pole type Rotor- In this type of rotor the poles and the winding are fitted on the shaft, as laminated cores are tied together with nut-bolts to form the core the pole-shoes are built up of steel or cast iron the field winding are connected in series D.C. supply is used for the excitation of the field.
Characteristics
(a) the diameter of the pole is kept greater then the length of the pole.
(b) two-third part of the cores is slotted and the remaining one-third part serve as pole base.
(c) laminated cores used to reduce eddy current losses.
(d) Damper-winding are field on the pole ends to stop hinting.
(e) this type of rotor is suitable for low speed alternators such as water turbine alternator.
(f) The number of pole is kept between 40 to 60 and is can be varied in accordance to the output power of alternator.
(b) Cylindrical Pole Type Rotor- its construction is similar to that of a d.c. armature it is usually made up of solid steel core. slots are cut all around its circumference in which field winding are placed as
Characteristics
(a) it is light in weight hence it can rotate at a high speed.
(b) it has low winding losses.
(c) its diameter is less in comparison to its length.
(d) it has only two or four poles. upto 50 MVA (Megavolt ampere) two poles are used, and upto 200 MVA, four poles are used.
3. Slip-rings- two slip-rings made up of copper or brash are used for the excitation of the filed with D.C. slip rings are mounted on the shaft of rotor and they make sliding contacts with the brushs.
4. Exciter- The device used to excite the filed is termed as exciter A d.c. shunt or compound generator of 120 to 250 volts is used as exciter in small alternators the exciter is mounted on the shaft of the alternator A variable resistor which is called a field regulator is connected in series with the shunt field as to control the speed of the rotor.
Why Alternator are Rated in kVA instead of kW ?
The power rating of a machine is defined as the power which a machine can deliver safety and efficiently. the output of a d.c. machine is simply expressed in kW, which indicates the kilowatt load, on which the machine can run without overheating and any damage to the insulation of windings. in d.c. machine the copper loss in the armature (I2 a . Ra) depends on the magnitude of armature current and is independent of power factor. in a.c. machine the power factor has also to be considered which depend on the amount of reactive load connected to the machine. if more number of motor are used, then the reactive load will be more which will result in high alternator losses. let an alternator have a rating of 20 kVA. if there is no reactive load in the circuit, then it will deliver 20 kVA ×1=20 kW output since the power factor is unity. but when reactive loads are connected to the alternator, then let the new power factor be 0.8 now it will deliver 20 kVA × 0.8 = 16 kW only. thus 4 kW power is lost and the alternator is delivering less power then 20 kW. for this reason they are rated in kVA. if any consumer has more reactive loads then he will arrange to improve the power factor of his installation so as to maintain the actual power rated in kVA.
(A) Alternator- An a.c. generating machine, is called an alternator or a.c. generator. It is used to generate alternating e.m.f. in accordance with the Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction- 'whenever a conductor is rotated in a magnetic flux, then it cuts the magnetic lines of force, and an e.m.f. is induced in it.' the working principle of an alternator is the same as that of a d.c. generator. an alternator requires a magnetic flux, conductor and the mechanical power for generating the e.m.f. the e.m.f.generated by the alternator is obtained through slip-ring or directly from the stator windings. depending on the type of alternator used. generally the field of an alternator is excited with a d.c. generator, which is mounted on the alternator's shaft. hence an alternator is also known as a separately excited generator.
(B) Types of Alternators-
1. On Basic of prime mover
a. Water Turbine Alternator
b. Steam Turbine Alternator
c. Oil Engine Alternator
2. On Basic of Phases
a. Single Phase Alternator
b. Three Phase Alternator
3. On Basic Of Rotor
1. Rotating Armature Alternator
2. Rotating Field
1. On the Basic of Prime Mover
a. Water Turbine Alternator- In this alternator, the rotor is rotated with the force of water. the water is stored in the form of a small lake,, by making a barrage on a river or canal. then a water-fall is produced with the stored water, which rotates the turbine and which in turn rotates the rotor. the speed of this alternator is low due to low water speed, and thus to obtain the reuired frequency, the number of poles is to be kept more,
Water Turbine Alternator
b. Steam Turbine Alternator- The force produced by steam is greater than produced by water. the steam operates a steam-engine and the engine operates the alternator. the speed of this alternator in high. A2-pole alternator can generate a frequency of 50 c/s at 3000 R.P.M.
Steam Turbine Alternator
c. Oil Engine Alternator- In this alternator, the rotor is rotated by a diesel or petrol operated engine. since the system is expensive, therefore, it is used for such purposes where water or steam type alternators do not suit or for emergency purposes.
2. On Basic of Phases
a. Single Phase Alternator- A small alternator used to generate the e.m.f. upto 250 volts. for light and fan purposes, is usually single phase type.
b. Three Phase Alternator-This alternator can generate 650 to 6600 or even more. It is used for light and fan as well as for power purposes.
3. on the basis of rotor
(1) Rotating Armature Alternator- It is similar to a generator. it employs slip-rings in place of commutator. the poles are kept stationary, and the armature rotates between the poles. the e.m.f. is obtained through the slip-rings. this alternator, usually has a low output capacity.
(a) Rotating field is comparatively light in weight and hence it can run at a high speed. two slip rings of low current capacity are sufficient for its field excitation circuit.
(b) higher voltage can be generated because of high speed of the rotor.
(c) It is easier to insulate armature coils designed to work at high voltage, because these are placed in the stator portion. if the armature is kept rotating, then the high insulation of armature coils will make it bulky. Hence it will not be able to rotate at a high speed.
(d) the armature winding placed in star or delta system, can directly be connected to the distribution cables.
Advantages of Polyphase Alternator
(a) Polyphase alternator are small in size and economic in comparison to the single phase alternators, having the same output, voltage and frequency.
(b) Polyphase alternator has a constant armature reaction, while a single phase alternator has a pulsating armature reaction under balanced load conditions:
(c) Polyphase transmission lines require less copper, in comparison to single phase transmission lines.
(d) the output power of a polyphase alternator is stable and non-pulsating for balanced loads.
(e) A polyphase alternator has a grater efficiency in comparison to a single phase alternator.
Working Principle Of Alternator
A conducting loop ABCD placed in the magnetic field of N and S poles. the loos is connected to two slip-ring S1 and S2. the a.c. output is taken from the two brushs, which make a sliding contact with the two slip-rings S1 and S2. here AB conductor is in from of N pole and BC conductor is in front of S-pole. since the loop is parallel to the flux thus it does not cut any flux when the loop is rotated in a clockwise direction by 30o , 60o and 90o and so on, then AB conductor cuts the flux in the upward direction while CD conductor cuts in down-ward direction.
Working Principle Of Alternator
the e.m.f. induced in AB part is collected by S1 and that in CD part by S2. the induced e.m.f. reached at its positive peak value in 90o rotation and then it reduced from peak to zero as
A.C. Cycle
after 1800 rotation of the loop, AB conductor reaches in from of S-pole while CD in front of N-pole. now further rotation to (-) 90o produced negative e.m.f. which reaches to negative peak and then back to zero. in this way, the loop completes one cycle. it is evident that the e.m.f. generated is A.C. whose direction and magnitude is changing at a definite rate.
Construction Of Alternator
The parts of an alternator are as follows:
1. Stator 2. Rotor
3. Slipring 4. Exciter
1. Stator- In a rotating field alternator, the stator contains the armature it is house in a cast-iron Yoke. it consists of laminated sheet-sheel cores.
Construction of Armature Cores
the slots are cut on the whole circumference of the cores as the cores are insulated with varnish or paper and tied together with nutbolts then these are fixed on the yoke or frame. armature winding are placed in the slots the may be cut in various shapes as
Various Shapes Of Slots
2. Rotor- The rotating part of a machine is termed as rotor hare it house the field winding and the poles. rotors are of following two types:
(a) Salient pole type (b) Cylindrical Pole Type
(a) Salient Pole type Rotor- In this type of rotor the poles and the winding are fitted on the shaft, as laminated cores are tied together with nut-bolts to form the core the pole-shoes are built up of steel or cast iron the field winding are connected in series D.C. supply is used for the excitation of the field.
Salient Pole Type Rotor
Characteristics
(a) the diameter of the pole is kept greater then the length of the pole.
(b) two-third part of the cores is slotted and the remaining one-third part serve as pole base.
(c) laminated cores used to reduce eddy current losses.
(d) Damper-winding are field on the pole ends to stop hinting.
(e) this type of rotor is suitable for low speed alternators such as water turbine alternator.
(f) The number of pole is kept between 40 to 60 and is can be varied in accordance to the output power of alternator.
(b) Cylindrical Pole Type Rotor- its construction is similar to that of a d.c. armature it is usually made up of solid steel core. slots are cut all around its circumference in which field winding are placed as
Cylindrical Pole Type Rotor
Characteristics
(a) it is light in weight hence it can rotate at a high speed.
(b) it has low winding losses.
(c) its diameter is less in comparison to its length.
(d) it has only two or four poles. upto 50 MVA (Megavolt ampere) two poles are used, and upto 200 MVA, four poles are used.
3. Slip-rings- two slip-rings made up of copper or brash are used for the excitation of the filed with D.C. slip rings are mounted on the shaft of rotor and they make sliding contacts with the brushs.
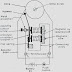
4. Exciter- The device used to excite the filed is termed as exciter A d.c. shunt or compound generator of 120 to 250 volts is used as exciter in small alternators the exciter is mounted on the shaft of the alternator A variable resistor which is called a field regulator is connected in series with the shunt field as to control the speed of the rotor.
Why Alternator are Rated in kVA instead of kW ?
The power rating of a machine is defined as the power which a machine can deliver safety and efficiently. the output of a d.c. machine is simply expressed in kW, which indicates the kilowatt load, on which the machine can run without overheating and any damage to the insulation of windings. in d.c. machine the copper loss in the armature (I2 a . Ra) depends on the magnitude of armature current and is independent of power factor. in a.c. machine the power factor has also to be considered which depend on the amount of reactive load connected to the machine. if more number of motor are used, then the reactive load will be more which will result in high alternator losses. let an alternator have a rating of 20 kVA. if there is no reactive load in the circuit, then it will deliver 20 kVA ×1=20 kW output since the power factor is unity. but when reactive loads are connected to the alternator, then let the new power factor be 0.8 now it will deliver 20 kVA × 0.8 = 16 kW only. thus 4 kW power is lost and the alternator is delivering less power then 20 kW. for this reason they are rated in kVA. if any consumer has more reactive loads then he will arrange to improve the power factor of his installation so as to maintain the actual power rated in kVA.
Alternator With Exciter















Nice bro
ReplyDeleteOsm Bro...
ReplyDelete1 no bhai
ReplyDelete