electrical measuring instruments
1. Classification Of Measuring Instruments
The electrical measuring instrument are classified in the following:
1. According to Use:
- Galvanometer
- Ammeter
- Voltmeter
- Wattmeter
- Energy meter
- Ohm meter
- Megger
- Avometer(multimeter)
- Maximum demand indicator
- Power factor meter
- Frequency meter
- Post office box
- Wheatstone bridge
2. According To Characteristics
(A) Absolute instrument
(B) Secondary instrument
(A). Absolute instrument: the instrument which indicates the presence of an electrical quantity by its deflection is termed as absolute instrument. these instrument are suitable for laboratory use only,e.g. tangent galvanometer.
(B). Secondary instrument: The instrument which measures an electrical quantity on a calibrated scale is termed as Secondary instrument. these instrument measure large values of electrical quantities. most of the measuring instrument which are used generally are of Secondary type. they are further classified as follows.
- Indicating Instrument
- Recording Instrument
- Integrating Instrument
- Indicating Instrument: It has a pointer which indicates the value of the electrical quantity on a calibrated scale at the time of measurement. it measures circuit, voltage, power, and resistance with an ammeter, volt-meter, energy meter and ohm meter respectively.
- Recording Instrument: It records an electrical quantity on a graph for a specified time. It has an ink-pen, which moves in a horizontal direction at a low uniform speed, while it remains erect on the graph paper. it is used at power generating stations for maintaining the record of variation if frequency or power factor etc.
- Integrating Instrument: It measures the power consumed in an electrical circuit a specified time. it may be an ampere-hour meter, watt-hour meter or a kilowatt-hour.
3. According to working Principle.
- Electromagnetic Instrument- Moving coil and moving iron instrument belong to this category.
- Electrodynamic Instrument-Dynamo, type ammeter, voltmeter and wattmeter belong to this category.
- Electrothermal Instrument- hot wire ammeter and thermo couple meters belong to this category.
- Electroinduction Instrument- Wattmeter and energy meters belong to this category.
- Electrochemical Instrument-D.C. ampere-hour meter and watt-hour meter belong to this category.
- Electrostatic Instrument- Certain voltmeters belong to this category.
- Spring Control: The spindle of the moving system rests on two pivots. A hair spring made of phosphor bronze wire is attached to the spindle. the spring is wound in a direction which is opposite to the rotation of pointer. Under the influence of defecting force, when the pointer moves, then the spring gets twisted in the opposite. as the deflecting force becomes zero, the twist of the spring bring brings back the pointer to its zero position. A spring used in instruments should have the following characteristics.
(b) It should have a low resistance.
(c) It should have a low temperature coefficient.
Spring Control
- Gravity Control: In this system, the pointer should rotate in a vertical plane. the control is obtained by scale attaching a control weight to the pointer in such a way that it produces a controlling torque because of change in its position, as balance weight is also attached to the pointer as both the weights should be adjustable. the controlling torque is proportional to the sine of the controlling torque is proportional to the sine of the angle of deflection and hence the scale will not be a uniform scale.
Gravity Control
Advantages
(a) The system is cheap.
(b) It is not affected by change in temperature.
(c) Its working life is long enough.
(d) it requires very maintenance and that too is inexpensive.
Disadvantages
(a) The instrument has to be kept in vertical position.
(b) The scale is cramped and non-uniform.
(c) The instrument has to be install in ground level.
- Air Fiction Damping
- Fluid Friction Damping
- Eddy Current Damping
Air Fiction Damping
(2) Fluid Friction Damping: This system is similar to the air friction damping, but it employs a liquid in place of air. the liquid should have a high viscosity so as to produce sufficient damping force. the system is not suitable for portable instrument, hence it is outdated now.
Fluid Friction Damping
(3) Eddy Current Damping: In this system, a circular thin disc of copper or aluminium is mounted on the spindle.A damping magnet is placed on side of the disc. the magnet is placed in such a way that the rotating disc will cut the magnetic lines of force of the magnet. thus, eddy current will be induced in the disc which will copper its motion and thus a damping force is produced in the instrument.
Fluid Friction Damping
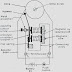
Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Instrument: this instrument work on the principle of a d. c. motor, i.e, a current carrying conductor which is placed in a magnetic field will be subject to a force couple, acting on it. In this way, conductor will try to rotate. the instrument consist of a powerful permanent magnet with soft iron pole pieces.A cylindrical iron core(or former) is mounted between the two poles of the magnet.
Permanent Magnet Moving Coil Instrument












best of luck bro
ReplyDelete