what is earthing
Earthing and its Purpose
(A) Earthing
The electrical potential of the earth is considered to be zero. Therefore, on connecting any electrical system to the earth, the voltage of the system will become zero. The process of burying a copper or G.I. plate at a depth of 2.5 to 3 metres or at the damp depth is known as earthing. Any electrical system or conductor having a voltage of any magnitude, which comes in contact with the earth point, will reach at zero voltage, because the voltage of earth point is zero.
(B) Aims of Earthing
(1) Safety of Human Life- The metallic cover of an electrical appliance may become Live due to leakage of electric current. The leakage may occur due to loss of insulation of conducting wires, loose connections or any other reason. A live metallic cover of a machine etc. may cause a serious shock to the Operator of the machine. But, if the cover is properly earthed, then it will not harm the person who comes in contact with the machine accidentally or purposely.
(2) Voltäge Stabilization- order to obtain a stable voltage, the neutral point of a transformer or an alternator is always earthed.
(3) Safety from Atmospheric Electricity- All large and tall buildings are necessarily provided with a lighting arrester, which is properly earthed. It passes all the space or atmospheric electricity near the building to the earth. In this way, it protects the building against any possible damage to the building and its residents.
(4) Protection of Overhead Electrical Installations- All over-head machines and installations are provided with a perfectly earthed lightning arrester.
(v) Earth as a Line- In telegraph communication, the earth is used as a return line, and thus it saves the expenditure of one wire.
(C) Possible Damages in the absence of Earth
- Leakage of electric current in any equipment will be able to cause a severe shock to the person accidentally coming is contact, even such person may die.
- Large and tall buildings will be able to be destroyed within a few moments by atmospheric electricity.
- The line voltage will not stand stable in the absence of neutral being earthed.
Effects of Electric Current on Human Body
Human body is greatly affected by the flow of A.C. or D.C. through it. The resistance of a human body under dry condition is generally 50,000 ohms/cm? while under wet condition it may reduce upto 700 to 1000 ohms per square centimetre.
Definitions
- Earthed Object- Any body connected to the earth point or earth electrode is called the earthed object. A good earth should have a direct connection with the earth electrode and rot through a switch, fuse etc.
- Earth Electrode- The metallic pipe, water pipe or any other conductor buried in the earth, as per I.E. Rules, is termed as earth electrode.
- Earth Continuity Conductor- Any wire, clamp, cable, conduit pipe, cable's metallic covering, earth lead or earth terminal of an electrical installation which is connected to the earth electrode is called earth continuity conductor.
- Earth Lead- The wire connected to the earth electrode is termed as earth lead or earth wire.
- Live- Any wire or conductor having a potential difference with the earth is called a live conductor.
- Earthed Supply- A neutral point is not a good earth point unless it is not connected to earth. The conductor wire used for joining the neutral point to the earth electrode is called the earthed supply.
Resistance of Earth Electrode
Any earth electrode passes the electric current into earth. The soil of the carth opposes the flow of current through it. Therefore, opposition offered by the soil is called the resistance of earth electrode. It varies in accordance with the type of soil present around the electrode. The resistivity bli for rocky soil is 5000 ohms-cm; for wet sandy soil it is 13000 ohm-cm and for ordinary soft oil it is 3000 ohm- cm. Arrangement should be made to keep a low resistance around the earth electrode for obtaining a good earth point.
Common Methods of Earthing
The common earthing methods are as follows
- Plate earthing
- Pipe earthing
- Rod earthing
- Earthing through a water pipe
- Earth plate
- Earth wire
- Earth pipe with socket
- Nut, bolt and washer
- Salt, charcoal and water
- Earth Plate- It is a G.I. (Galvanised iron) plate of 60 cm x 60 cm x 6.3 mm size or a copper plate of 60 cm x 60 cm x 3.18 mm size.
- Earth Wire- It is a G.I. or tinned copper wire. For G.I. plate G.I. wire and for a copper plate a copper wire is used. For light and fan purposes a wire of 12 to 14 S.W.G. and for power purposes a wire of 8 to 10 S.W.G. is suitable.
Common Method of Plate earthing
- Earth Pipe with Socket- It is a G. I. pipe of 12 mm to 30 mm diameter. Its length should be such that it may reach upto the plate from the ground level. A covering socket is screwed at the top of the pipe, so that the dust and waste etc. may not enter into the pipe. If necessary, then water may be poured in the pipe by opening the socket, so as to keep the soil damp.
- Nut, Bolt and Washer- G. I. nut, bolt and washers are used for tighting the wire to the plate.
- Salt, Charcoal and Water- These materials are used for maintaining the dampness and thus a low resistance of the soil around the plate.
Earthing Procedure- A pit is dug in the ground upto a depth of 2-2.5 metres or upto a damp depth. The earth plate is buried in the pit alongwith the salt and charcoal, An earth wire is bolted to the earth plate, before burying it in the pit uoi with the help of nut, bolt and washer. The earth wire is taken out to make an earth point through the G.I. pipe. Some water is poured in the pit through the pipe, so as to increase the conductivity of the soil around the earth plate. Now the covering socket is closed, and the earth point is ready for use.
2. Pipe Earthing- In this method a cast iron pipe of 30-75 mm diameter and 2.5-3.0 metres length is buried in the pit alongwith the salt and charcoal The pipe should have sufficient holes at its surface, so as to maintain the dampness inside the pipe. An earth wire is tied near the top of the pipe with the help of a clamp. In order to have an effective earth, one or two buckets of water may be poured in the pipe, especially in the summer season. This method has an advantage that the earth wire can't break easily from the pipe, while in plate earthing method the wire can break due to slight carelessness.
Common Method of Pipe earthing
3. Rod Earthing- In this method, 4-5 solid zinc or copper of 12-20 mm diameter and 1-1.5 metre length are hammered in the ground. The rod having a pointed tip is hammered first and then the second one is screwed over the first with the help of a socket. The second one is also hammered in the ground and then the third one is screwed over it. The same procedure is repeated till the pointed rod does not reach at the damp depth. The more is the depth of the rod, the lower will be the resistance of earth. An earth wire is tied near the top of the rod with the help of a clamp. This method has the advantage of being economical and quick.iw 4. Earthing through a Water Pipe-In this method, a stranded copper wire is clamped or tied and soldered on the G.I. pipe of a hand-pump. Since, a hand-pump reaches upto the water-bed inside the earth, thus it will serve the purpose of a good earth electrode. The earth wire must not be loose, otherwise the hand pump will cause a dangerous shock to the person who will touch it.
Method of Good Earthing for a Sub-station
As per I.E. rules, there are two methods of earthing which are used commonly now-a-days. The methods are as follows :
- Plate earthing
- Pipe earthing
- Copper or G.I. earth plate
- Copper or G.I. earth wire
- Copper or G.I. nut, bolt and washer
- Funnel
- G.I. pipe
- Cast iron cover
- Salt, charcoal and water
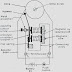
Plate earthing for a sub-station
An earth wire is bolted to the earth plate with the help of nut, bolt and washer. The earth wire and the nut bolts and washer should be of the same metal as of the plate used. A 15 cm thick layer of salt and charcoal is placed around the earth plate, so as to reduce the earth resistance and to maintain dampness. A G.I. pipe of 19.05 mm diameter is fitted over the plate. A funnel with a wire-mesh cover is placed at the top of the pipe, and the whole arrangement is covered with a cast iron cover, as shown in Fig. 19.3. In order to maintain the moistness around the earth plate, 3 or 4 buckets of water is poured in the pipe through the funnel. This system has a disadvantage, i.e. if the earthing wire gets broken inside the ground, then it can only be replaced by re-digging the pit.
(2) Pipe Earthing- This method employs only a pipe instead of a plate for earthing. A G.I. pipe of 38 mm diameter and 2 metres length is buried in a 4.75 m deep pit. The pipe should have sufficient 12 mm diameter holes at its surface. Now the pit is filled with alternate layers of salt and charcoal upto a distance of 15 cm around the pipe, A G.I. pipe of 19 mm diameter is fitted above the 2 m pipe. In order to maintain the moisture around the main pipe, 3 or 4 buckets of water is poured in the pit through a funnel, which is placed at the top of the thin pipe. The earthing lead of 12.7 mm diameter G.I. pipe is clamped near the top of the thin pipe. A G.I. or copper strip of large cross-sectional area may be used as earth lead for earthing the high power machines.
Pipe earthing for a sub-station
The pipe earthing is better than plate earthing, because it can earth more leakage current, and the possibility of a breaking in the earth wire is minimum.
The earth wire resistance should not be more than one ohm in case of copper earthing and 3 ohms in case of G.I. earthing as per I.E. Rules. If an earth electrode has become less effective, then pour 2-3 buckets of water through the funnel. Even if the earth electrode is not functioning at all, then it should be re-conditioned in the same manner as use.! in pipe earthing.
I.S.I. Specifications Regarding Earthing
The specification regarding earthing as prescribed by I.S.I. (Indian Standard Institution) are as follows :
- The earth electrode should be installed at a place at least 1.5 metre away outside the building whose installation system is being earthed.
- The earth wire should be of the same metal as that of the earth electrode to avoid electrolytic action.
- The minimum cross-sectional area of the earth wire should not be less than 13 mm? (i.e. 8 S.W.G,). and not more than 65 mm? (i.e. 7 S.W.G.).
- The size of the earth conductor as a general rule should not be less than half of the cross-section of a live line conductor, In residential buildings a 14 S.W.G. bare copper wire is recommended as earth wire.
- Charcoal and salt mixture should be filled around the earth electrode for effective earthing.
- The size of the earth wire run for earthing should be such, as to carry full load current of the installation and offer least resistance to the flow of leakage current.
- The earth wire should be taken through G.I. pipe of 12 mm dia., for at least 32.5 cm length above and below the ground surface, to the earth electrode against mechanical wear and tear.
- The earth wire connected to the earth electrode should not be necessarily run along the whole wiring system. All the earth wire run along the sub-circuit should be terminated and looped firmly at the main board, and from where the main earth wire should run to the earth electrode. These loop earth wires should be of 14 S.W.G. (6.16 mm?) cross-section or half the size of the subcircuit conductor, whichever of the two is least.
- The earth electrode should always be placed in vertical positions inside the earth or pit, so as to be in contact with all the different earth layers.
- The nut, bolt and washer should be of the same metal as that of the earthing electrode.
Indian Electricity Rules Rule 33- The earth terminal at the consumer's house: 1. As per rule 58, the supplier must provide a proper earth terminal for the use of consumer near or within reach the commencing point of supply.
- The consumer using medium, high or extra high voltages must provide his own earthing system with an independent earth electrode and maintain it carefully.
- If the supplier is satisfied with the earthing system provided by the consumer, then he should not provide a separate earth terminal to the consumer from his earthing system already installed on 30th June 1966 or before.
Rule 61- Connection to the earthing system :
- For a medium voltage installation system where voltage is more than 125 volts, the connection to the earthing system will be governed by the following provisions :
(b) In case of a concentric cable electric supply system, o the outer metallic conductor of the cable must be separately earthed at two places, i.e., at the commencing and the terminating ends of the supply line. (c) An earth line link can be placed for testing or fault detection purposes by temporarily breaking the earth line at the link.
(d) (1) In the D.C. 3-wire system, the middle conductor must be earthed at the generating station only, and the leakage current from the middle conductor to the earth terminal shall be recorded continuously by a recording ammeter. If at any instant the leakage current exceeds above the 1/1000th part of the supply current, then immediate arrangements will have to be made to improve the insulation of the system.
(2) In case the middle conductor is earthed through a circuit breaker with a shunt resistance, the value of the resistance must not he more than 10 ohms. In case the circuit breaker becomes open-circuited, then immediate arrangements will have to be made to improve the insulation of the system, and the circuit breaker must be short-circuited as soon as possible.
(3) In case of the resistance type earthing system, an ammeter should be used as a safety measure, and the arrangements will have to be made to detect the faulty earthing and to remove the defect immediately.
(d) In A.C. system, impedance cut-out or circuit breaker should be placed in the earth line (except where switch-gears or instruments are used for breaking), and the supplier will have to keep the record of the earth leakage current (if any) for deciding the result of the test made. (0 Any consumer should not be allowed to connect his earth line to a water main line without the concept of the electrical inspector and the owner of that line.
(e) In A.C. system also the earth line may be connected in the above manner provided that each earth line is tied or clamped properly with the metallic sheathing or metallic armouring (if any).
2. All generators, stationary motors, frames of portable motors and other such machines, all transformers and other such equipments, all regulating and energy controlling equipments, and metallic coverings of all medium voltage energy consuming equipments must be provided with two separate and proper earth terminals by the consumer.
3. All the metallic casings or metallic coverings, through which an electric supply line is passed or which are fitted to any electrical equipment for its safety purpose, must be connected to an earth terminal in such a way that a good electrical and mechanical earth contact is assured, through-out the length, alongwith the junction boxes and such other open parts.
Subrule
(1) In case of low voltage supply line, the above rule shall not be applicable to wall brackets and tubes, controllers, switches, ceiling fans, regulator covers, and other accessories (except portable hand- lamps and other portable or transportable appliances) unless an earth terminal is not provided. Sub rule
(ii) In case of low voltage supply line, all wall sockets will be of 3-pin type and the third pin will be earthed properly and permanently. This sub-rule shall be applicable to all new electrical installations, but in case of an addition to an existing installation the provisions of the sub-rule shall have to be fulfilled within two years from the date of its enforcement.
4. Before supplying electric current to an electric supply line or an electrical equipment, all earthing systems shall be tested for its insulation resistance, so as to ensure that a good earth has been provided.
5. The insulation resistance of all earthing systems provided by a supplier should be tested atleast once within a period of two years on a dry day of the dry season.
6. The supplier will have to maintain a record of each earth test and to submit the report alongwith the result of the test, to the inspector as and when required by him following the date of test and within two years.
Rule 62- Medium voltage system : When the medium voltage is in use then the voltage present between the earth and the conduction of the system should not be more than the normal voltage present between them.
Rule 67- High and extra high voltage:
- The neutral line should be earthed separately at two places, one at the generating station and the other at the substation.
- If concentric cable has been used in an electric supply line, then the outer conductor of the cable should be earthed.
Rule 90-
- In overhead line, each metallic pole, supporting or associated with the pole installation (except live conductors) must be earthed.
- Every stay-wire should be earthed, provided an insulator is not placed in it at a height of 3.05 m from the ground level.










No comments
If You Have Any Doubts, Please Let Me Know